Digital PCR Solution for Quantitative Analysis of GMO products
With the continuous expansion of the planting area of genetically modified crops in the world, the types and quantities of genetically modified products have gradually increased. The debate on the safety of genetically modified crops and their processed foods has swept the world rapidly, making people full of doubts about the safety of genetically modified crops and their products. Subsequently, the governments of various countries have issued a series of regulations and laws and regulations on the management of genetically modified crops and their products. Many countries also stipulate that genetically modified products with a genetically modified content reaching a certain threshold must be labeled. Rapid and accurate GMO detection technology is an important tool for the safety supervision of GMO products. Therefore, establishing a fast, simple, high-sensitivity, high-precision, and absolute quantitative detection method for GMO components has become a hot issue in current research.
The copy number content of exogenous genes (strain-specific sequences) and plant endogenous genes of transgenic plants can be directly obtained through digital PCR amplification reaction. The copy number ratio (percentage) of the exogenous gene and the endogenous gene in the sample DNA is the relative percentage of the corresponding transgenic plant line in the sample.
Digital PCR solutions for environmental samples (water body/atmosphere/soil, etc.), microbial analysis
Water is one of the most important resources on Earth and is essential to all life. Population growth and climate change will increase demand on existing but insufficient freshwater supplies. Consequently, in many parts of the world, treated wastewater is used not only for irrigation but also to supplement non-potable water supplies. However, the potential reuse of treated wastewater as a source of drinking water requires further attention and enhanced control of wastewater contaminants (i.e., pathogenic microorganisms) as they may pose health risks.
Waterborne and foodborne enteroviruses, posing a significant risk to public health. They are spread primarily by the oral-fecal route, either through ingestion of contaminated food and water, or through person-to-person contact. Given the low concentrations in which these viruses are found in the environment, it is critical to accurately determine the efficacy of wastewater treatment processes.
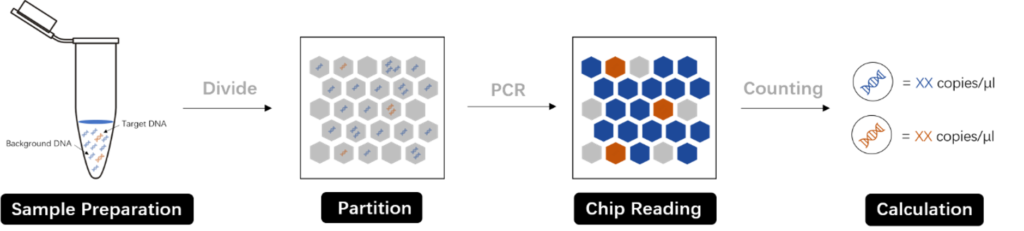
“Digital PCR dilutes target nucleic acid molecules into a large number of droplet units. Each droplet contains one or more, or does not contain target DNA templates. The droplet units are independently amplified in parallel. After the amplification, the target molecule template is contained. The microdroplets will give a fluorescent signal, and finally according to the Poisson distribution principle and the proportion of positive microdroplets, the analysis software can calculate the concentration or copy number of the target molecule. Therefore, the absolute quantification of the target molecule can be performed without a standard curve. “





